Allocation of resources for IGCSE Economics for 0455
To go to the ECONOMICS MIND MAP MAIN PAGE Click here
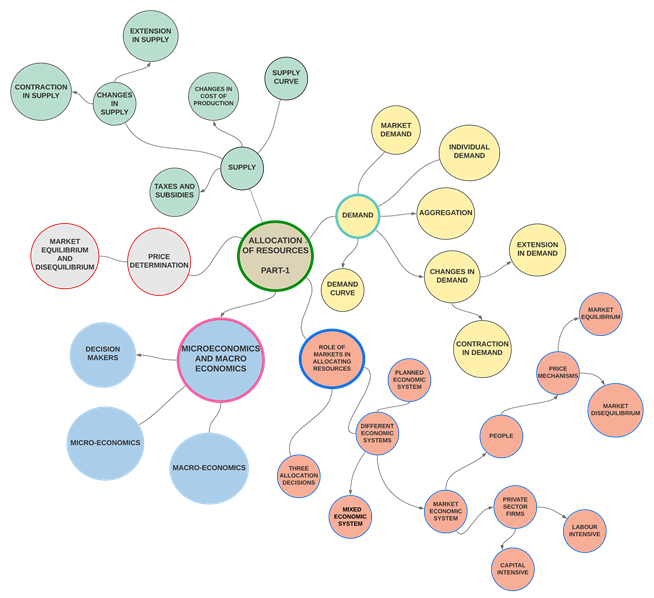
Allocation of resources — quick explainer
What allocation means
Answering the 3 decisions: what to produce, how to produce, for whom to produce.
Guided by demand, supply and the price mechanism .
Demand
Demand curve: shows quantity demanded at different prices.Changes in demand: shifts due to non-price factors.Movements: extension in demand (price falls) and contraction in demand (price rises).
Aggregation: individual demand combines to give market demand .
Supply
Supply curve: shows quantity supplied at different prices.Changes in supply: shifts from changes in cost of production , taxes and subsidies .Movements: extension in supply (price rises) and contraction in supply (price falls).
Price determination
Where demand meets supply gives the market equilibrium price and quantity.
Disequilibrium: excess demand or excess supply ? price adjusts.
Price mechanism
Prices act as signals and incentives for people and firms.
Guides choices between methods of production: labour intensive vs capital intensive .
Explains outcomes like market equilibrium or market disequilibrium .
Different economic systems
Planned economic system (government decides).Market economic system (decisions via markets and prices).Mixed economic system (both government and markets).
Micro & Macro + decision makers
Micro-economics: decisions by individuals and firms.Macro-economics: whole-economy outcomes (growth, inflation, jobs).Decision makers: consumers, workers, firms, government.
How it all connects
Demand + Supply ? equilibrium price ? resource allocation through the price mechanism.Individual choices aggregate to markets; economic systems shape how decisions are made.
Write a public review