 Download PDF
Download PDF
This page has diagram based questions for IGCSE Biology-Topic:Excretion
So lets begin the revision using the diagrams. happy learning!
Topic 1- Excretion in humans
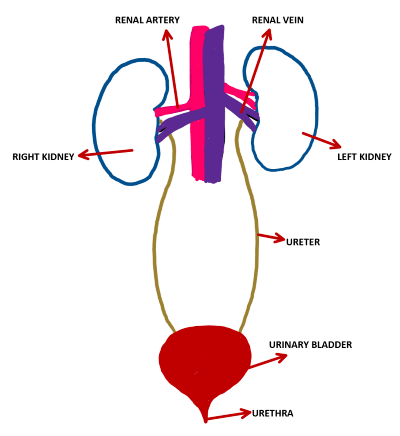
- The excretory system consists of organs which remove metabolic wastes and toxins and other substances in excess of their requirements.
- In humans, this includes the removal of urea from the bloodstream and other wastes produced by the body.
- The removal of urea happens in the kidneys, while solid wastes are expelled from the large intestine.
- The excretory system in humans consists mainly of the kidneys and bladder.
- The kidneys filter urea and other waste products from the blood, which are then added to the urine within the bladder.
- Other organs, such as the liver, process toxins but put their wastes back into the blood. It is up to the kidneys to filter the blood so that toxic substances do not accumulate.
- Renal artery:The renal arteries carry a large portion of total blood flow to the kidneys. Up to a third of total cardiac output can pass through the renal arteries to be filtered by the kidneys.Renal artery carries mineral rich, oxygenated blood from the heart to the kidneys for nutrition and cellular respirationOxygenated blood comes to the kidneys from the right and left renal arteries off the abdominal aorta.
- Renal vein:Deoxygenated blood leaves the kidneys via the right and left renal veins that run into to the inferior vena cava
- Ureter:These narrow tubes carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder. Muscles in the ureter walls continually tighten and relax forcing urine downward, away from the kidneys. If urine backs up, or is allowed to stand still, a kidney infection can develop.
- Urinary blader:The bladder's walls relax and expand to store urine, and contract and flatten to empty urine through the urethra.
- Urethra:This tube allows urine to pass outside the body.
INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF THE KIDNEY:

Write a public review