CORE:
Describe the characteristics of living organisms by describing:
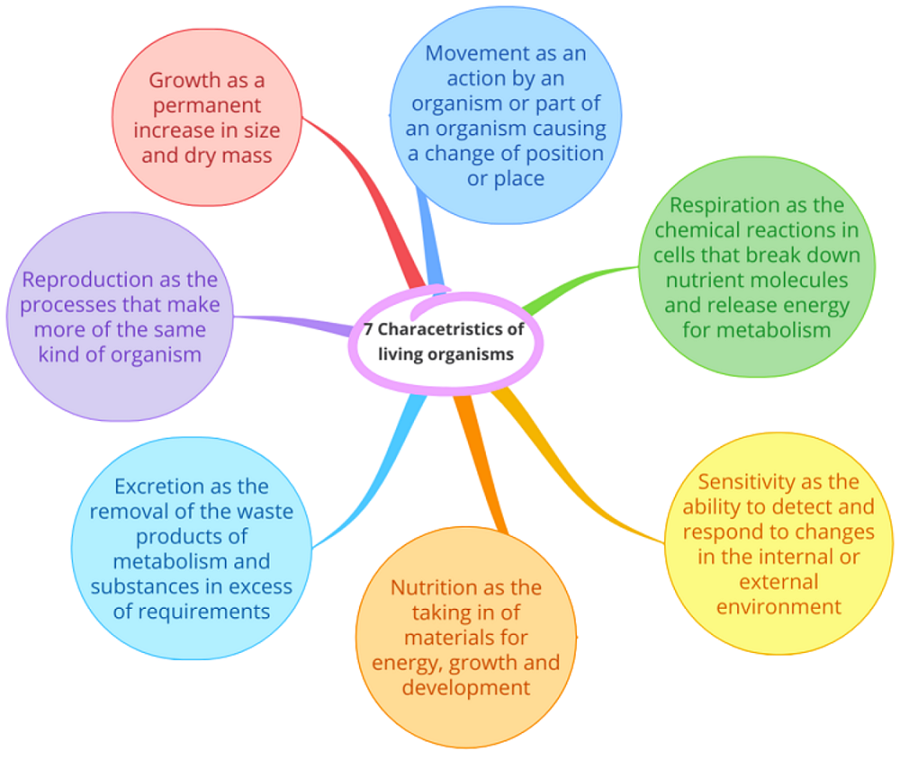
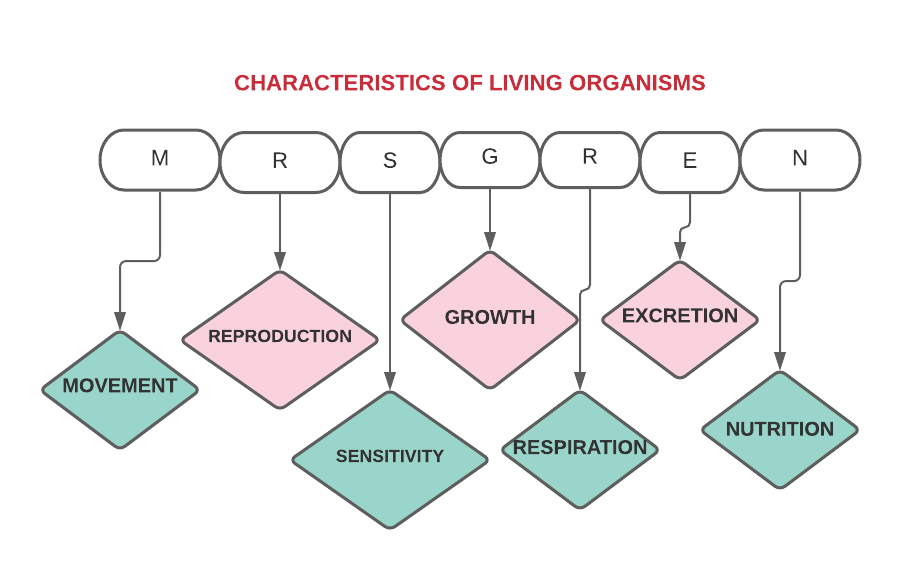
Following are the seven characteristics of living organisms:
1.Movement: It is an action by an organism or part of an organism causing a change of position or place.
2.Respiration: The chemical reactions in the cells that break down nutrient molecules and release energy for metabolism are called as respiration
3.Sensitivity: It is the ability to detect and respond to changes in the internal or external environment.
4.Growth: It is the permanent increase in size and dry mass
5. Reproduction: Processes that makes more of the same kind of organism.
6. Excretion: It is the removal of the waste products of metabolism and substances in excess of requirements.
7. Nutrition: It is the taking in of materials for energy, growth and development.
Note:
Skin, kidneys and lungs are the three major organs of excretion in humans:
1. Sweat glands in the skin produce sweat. This contains water, urea and salt. Excreting sweat helps keep the body cool in hot conditions.
2. The kidneys remove excess water, salts and urea to prevent a toxic build-up of these substances in the body.
3. The lungs remove excess carbon dioxide (and some water) when breathing out
Classification of organisms
1. Organisms can be classified into groups by the features they share.
2. Classification system aims to reflect evolutionary relationships.
3. Sequence of bases in DNA are used as a means of classification.
4.Group of organisms that share a more recent ancestor (are more closely related) have base sequences in DNA that are more similar than those that share only a distant ancestor.
Key definitions:
1.Binomial system of naming species: It is an internationally agreed system in which the scientific name of an organism is made up of two parts showing the genus and the species.
2. Species: It is a group of organisms that can reproduce to produce a fertile offspring..
3.Ingestion: It means to take in food from the mouth.
4.Egestion: Egestion is the discharge or expulsion of undigested material (food) from a cell in case of unicellular organisms, and from the digestive tract via the anus in case of multicellular organisms
1. The entire two-part name must be written in italics (or underlined when handwritten). •
2. The generic name (genus ) is always written first. •
3. The genus name must be capitalized. •
4. The specific epithet ( species name ) is never capitalized. Examples: Common name Scientific ( Generic ) name Modern humans Arabian camel African elephant Albatross Alpaca Asian Elephant Blackbuck Homo sapiens Camelus dromedarius Loxodonta africana Diomedeidae Lama pacos Elephas maximus Antelope cervicapra
Note: All scientific names have been derived from Latin
Some IGCSE Past Paper Questions for quick reference:
O/N/2014-P12-Q1 Ans: B
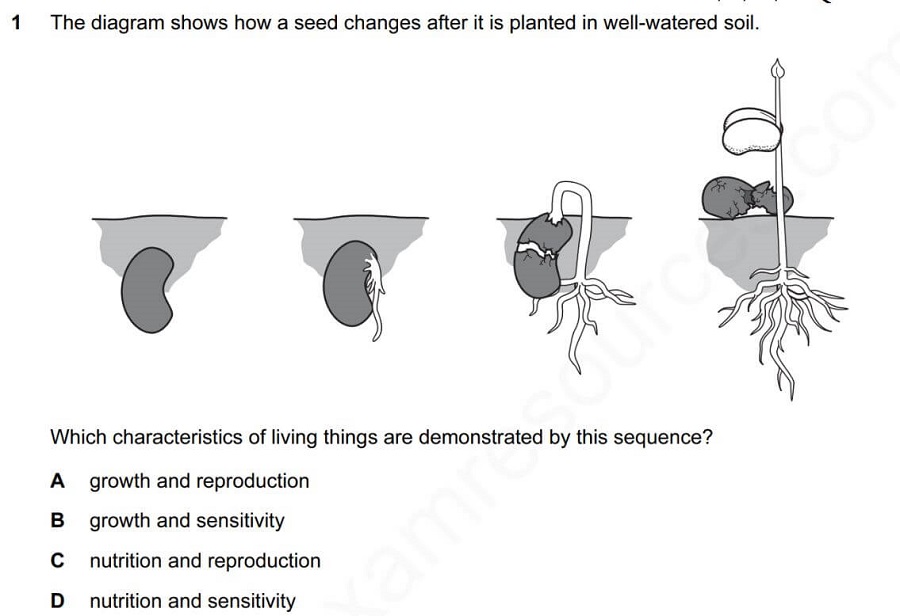
O/N/2015-P12-Q1 Ans: D

O/N/2011-P12-Q6 Ans: D

O/N/201-P12-Q7C

Links to member's Area IGCSE Biology Topic Questions and MarkSchemes :
IGCSE Biology Topic Questions Paper 2 Multiple Choice Questions and Mark Schemes
IGCSE Biology Topic Questions Paper4 Extended Theory Questions and Markschemes
IGCSE Biology Topic Questions Paper 6 Alternative to Practical Questions and Mark Schemes

NOTE: While learning definitions, strictly learn the definitions given as per your exam syllabus
Paper 2 Exam Tips:
On the whole, questions based on identifying the characteristics based on the diagrams are more common