IGCSE Chemistry Revision Notes Diffusion
Free download IGCSE Chemistry Diffusion Notes 2024 to 2028 Exams
1.2-IGCSE-Chemistry-Notes-States-of-Matter-Diffusion.pdf
DIFFUSION
Definition:
Diffusion is the random movement of particles from a region of their high concentration to a region of their low concentration down the concentration gradient.
Speed of diffusion depends upon the Mr( relative molecular mass): This means that the speed of diffusion of a gas depends on how heavy it's molecules are. Molecules with a lighter mass diffuse faster than those with a heavier mass.
FOR EXTENDED ONLY
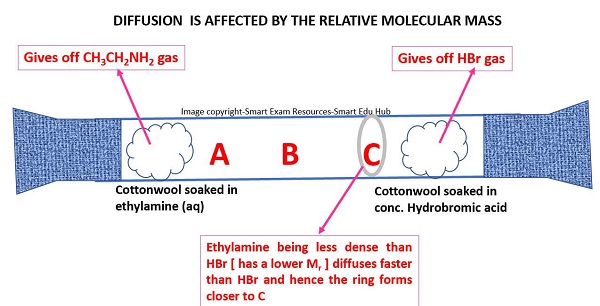
OBSERVATIONS
• The white ring is formed at C. This is because ethylamine less dense( or has is a lower Mr) than HBr. Hence ethylamine diffuses faster than HBr.
Why do the gases diffuse?-Explanation based on kinetic theory:
Gases diffuse because their particles move in random motion. These particles then collide .This diffusion is from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration.
Diffusion happens faster in warmer temperatures than in cooler temperatures.
APPLICATION BASED INFORMATION CREATED FROM PAST PAPER QUESTIONS:
- When a liquid spills on a floor and can be smelt far away it means that it has first evaporated then diffused.
- When a precipitate is formed during chemical reactions, the particles, diffuse, collide and then react
- Particles spread out evenly as a result of diffusion
- Sugar dissolves then diffuses. You cannot say sugar melts and then diffuses.
- Generally diffusion happens in liquids and gases as the particles are free to move. Their particles are constantly moving colliding and changing directions.
- Diffusion in gases is faster than diffusion in liquids because the gas particles move rapidly. They are able to move freely because kinetic theory assumes that there are no forces of attraction between the gas particles while there are weak forces of attraction between liquid particles.
- Diffusion does not happen in solids because the particles are tightly packed and they can only vibrate in their mean positions and not move about.
- Diffusion can occur in liquids which are miscible
- Diffusion is also possible in solids that dissolve in liquids.
- At the same temperature, the molecules that have the lower mass diffuse faster than the heavier molecules. If the lighter and heavier molecules have the same amount of energy when they collide, then, the lighter ones will bounce off the heavier ones at a faster rate. So, lighter molecules diffuse faster than the heavier molecules.

Write a public review