We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. We adhere to the GDPR and EU laws and we will not share your personal information with or sell it to third-party marketers. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it. Our privacy policy
Cookie policy Download PDF
Download PDF
IGCSE Chemistry Revision Notes
Topic:Atoms, elements and compounds
Sub Topic: 2.4 Ions and ionic bond
Syllabus Objectives:
Core :
EXTENDED/SUPPLEMENT
IONS AND IONIC BONDS
Formation of sodium chloride:
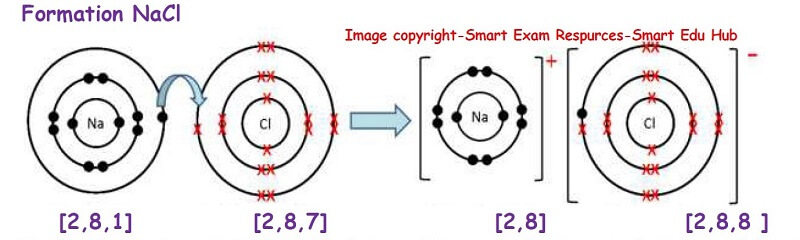
In the formation of sodium chlorine, sodium atom loses one electron and becomes a +vely charged cation. The chlorine atom accepts this electron and forms a negatively charged ion called the anion. Thus by doing so both the ions have a stable electronic structure which is the same as the noble gas. So a stable electronic structure has been formed.
Formation of calcium chloride:
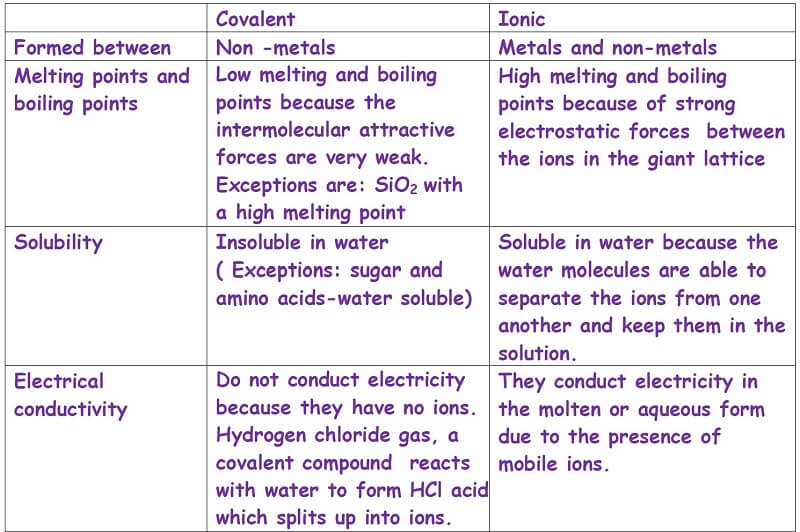
Ionic and covalent-Compounds-A comparison
The above video is a preview of the actual revision notes available as a part of the paid membership. All learning resources in the form of pdfs that are available on the website are 100% printable and downloadable.
- Smart Exam Resources

Write a public review